Vue学习笔记
初期
Es语法
箭头函数
// 箭头函数
let fun = (name) => {
// 函数体
return `Hello ${name} !`;
};
// 等同于
let fun = function (name) {
// 函数体
return `Hello ${name} !`;
};
定义箭头函在数语法上要比普通函数简洁得多。箭头函数省去了function关键字,采用箭头=>来定义函数。函数的参数放在=>前面的括号中,函数体跟在=>后的花括号中。
关于箭头函数的参数:
① 如果箭头函数没有参数,直接写一个空括号即可。
② 如果箭头函数的参数只有一个,也可以省去包裹参数的括号。
③ 如果箭头函数有多个参数,将参数依次用逗号(,)分隔,包裹在括号中即可。
then
- then()方法是异步执行。
- 意思是:就是当.then()前的方法执行完后再执行then()内部的程序,这样就避免了,数据没获取到等的问题。
- .then里的参数为then()前的方法返回的值
Vue定义
vue是一个单页面应用,即只有一个html文件
public/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">
<meta name="renderer" content="webkit">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no">
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
<title><%= webpackConfig.name %></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>
main.js
vue-cli首先是帮我们引入了vue和App组件,通过new Vue建立了一个Vue的实例对象,然后就通过$mount方法将这个Vue实例挂载到了一个 id 名为 app 的标签上,然后通过render函数将App组件插入到了这个标签内。
import enLang from 'element-ui/lib/locale/lang/en'// 如果使用中文语言包请默认支持,无需额外引入,请删除该依赖
import '@/styles/index.scss' // global css
import App from './App'
import store from './store'
import router from './router'
import './icons' // icon
import './permission' // permission control
import './utils/error-log' // error log
import * as filters from './filters' // global filters
/**
* If you don't want to use mock-server
* you want to use MockJs for mock api
* you can execute: mockXHR()
*
* Currently MockJs will be used in the production environment,
* please remove it before going online ! ! !
*/
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
const { mockXHR } = require('../mock')
mockXHR()
}
Vue.use(Element, {
size: Cookies.get('size') || 'medium', // set element-ui default size
locale: enLang // 如果使用中文,无需设置,请删除
})
// register global utility filters
Object.keys(filters).forEach(key => {
Vue.filter(key, filters[key])
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
项目结构
├── build // 构建相关
├── config // 配置相关
├── src // 源代码
│ ├── api // 所有请求
│ ├── assets // 主题 字体等静态资源
│ ├── components // 全局公用组件
│ ├── directive // 全局指令:除了v-bind这样的自定义指令v-demo
│ ├── filtres // 全局 filter,用于常见的文本格式化
│ ├── icons // 项目所有 svg icons
│ ├── lang // 国际化 language
│ ├── mock // 项目mock 模拟数据 需安装mockjs
│ ├── router // 路由
│ ├── store // 全局 store管理
│ ├── styles // 全局样式
│ ├── utils // 全局公用方法
│ ├── vendor // 公用vendor
│ ├── views // view,每个页面或者模块特定的业务组件则会写在当前 views 下面。如:@/views/article/components/xxx.vue。这样拆分大大减轻了维护成本。
│ ├── App.vue // 入口页面
│ ├── main.js // 入口 加载组件 初始化等
│ └── permission.js // 权限管理:全局路由守卫+登录判断
├── static // 第三方不打包资源
│ └── Tinymce // 富文本
├── .babelrc // babel-loader 配置
├── eslintrc.js // eslint 配置项
├── .gitignore // git 忽略项
├── favicon.ico // favicon图标
├── index.html // html模板
└── package.json // package.json
Vue.prototype
通过在原型上定义它们使其在每个 Vue 的实例中可用,不污染全局作用域
main.js
//$为防止被组件中相同变量覆盖
Vue.prototype.$appName = 'My App'
可以在所有vue实例中使用
new Vue({
beforeCreate: function () {
console.log(this.$appName)
}
})
示例
-
导入axios
// 插件——异步请求 axios import axios from 'axios' import './axios.js' Vue.prototype.$http = axios
Vue.use和Vue.prototype的区别
相同点:都是注册插件的方式,没有本质区别,都是在vue.prototype上添加了一个方法
不同点:vue.use适用于注册vue生态内的插件,vue.prototype适用于注册生态外的插件
Promise对象
常和axios结合在一起使用

通过打印可以看出Promise是一个构造函数,有all、reject、resolve、then、catch等方法。这样用Promise new出来的对象肯定就有then、catch等方法。
用Promise的时候一般是包在一个函数中,在需要的时候去运行这个函数,如:
created() {
this.testPromise()
},
methods: {
testPromise() {
var p = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
//做一些异步操作
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('Promise执行');
resolve('这是Promise返回的数据');
}, 2000);
});
}
}
test(){
//相当于 var p = new Promise(()=>{})
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
api
.then(data => {
//你的逻辑
resolve();
})
.catch(err => {
//返回错误
reject(err);
});
});
}
resolve和reject:Promise的构造函数接收一个参数,是函数,并且传入两个参数:resolve,reject,分别表示异步操作执行成功后的回调函数和异步操作执行失败后的回调函数。其实这里用“成功”和“失败”来描述并不准确,按照标准来讲,resolve是将Promise的状态置为fullfiled,reject是将Promise的状态置为rejected。
1、resolve:作用是把resolve的状态置为resolved,在resolve中返回Promise的数据。相当于普通函数的return。如果不需要返回数据,则resolve();即可。
2、reject:作用就是把Promise的状态置为rejected,这样在then中就能捕捉到,然后执行“失败”情况的回调。
Promise构造函数的参数是一个函数,函数里面的代码是异步的,即Promise里面的操作,和Promise()外面的操作时异步”同时”进行的。此外,只要在函数前面加上async 关键字,也可以指明函数是异步的。
async关键字实际是通过Promise实现,如果async 函数中有返回一个值 ,当调用该函数时,内部会调用Promise.solve() 方法把它转化成一个promise 对象作为返回,但如果timeout 函数内部抛出错误,那么就会调用Promise.reject() 返回一个promise 对象。若某函数调用一个异步函数(比如内部含有promise),该函数应用async修饰。
await表示“等待”,修饰返回promise 对象的表达式。注意await 关键字只能放到async 函数里面。
function doubleAfter2seconds(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(2 * num)
}, 2000);
} )
}//写一个async 函数,从而可以使用await 关键字, await 后面放置的就是返回promise对象的一个表达式,所以它后面可以写上 doubleAfter2seconds 函数的调用
async function testResult() {
let result = await doubleAfter2seconds(30);
console.log(result);
}
async和await的用法
async 表示函数里有异步操作,
await 表示紧跟在后面的表达式需要等待结果。
同 Generator 函数一样,async 函数返回一个 Promise 对象,可以使用 then 方法添加回调函数。当函数执行的时候,一旦遇到 await 就会先返回,等到触发的异步操作完成,再接着执行函数体内后面的语句。(非阻塞)
async
1)表明程序里面可能有异步过程: async关键字表明程序里面可能有异步过程,里面可以有await关键字;当然全部是同步代码也没关系,但是这样async关键字就显得多余了;
2)非阻塞: async函数里面如果有异步过程会等待,但是async函数本身会马上返回,不会阻塞当前线程,可以简单认为,async函数工作在主线程,同步执行,不会阻塞界面渲染,async函数内部由await关键字修饰的异步过程,工作在相应的协程上,会阻塞等待异步任务的完成再返回;
3)async函数返回类型为Promise对象: 这是和普通函数本质上不同的地方,也是使用时重点注意的地方; (1)return newPromise();这个符合async函数本意; (2)return data;这个是同步函数的写法,这里是要特别注意的,这个时候,其实就相当于Promise.resolve(data);还是一个Promise对象,但是在调用async函数的地方通过简单的=是拿不到这个data的,因为返回值是一个Promise对象,所以需要用.then(data => { })函数才可以拿到这个data; (3)如果没有返回值,相当于返回了Promise.resolve(undefined);
4)无等待 联想到Promise的特点,在没有await的情况下执行async函数,它会立即执行,返回一个Promise对象,并且绝对不会阻塞后面的语句,这和普通返回Promise对象的函数并无二致;
5)await不处理异步error: await是不管异步过程的reject(error)消息的,async函数返回的这个Promise对象的catch函数负责统一抓取内部所有异步过程的错误;async函数内部只要有一个异步过程发生错误,整个执行过程就中断,这个返回的Promise对象的catch就能抓取到这个错误;
5)async函数的执行: async函数执行和普通函数一样,函数名带个()就可以了,参数个数随意,没有限制,也需要有async关键字;只是返回值是一个Promise对象,可以用then函数得到返回值,用catch抓整个流程中发生的错误;
await
1)await只能在async函数内部使用:不能放在普通函数里面,否则会报错;
2)await关键字后面跟Promise对象:在Pending状态时,相应的协程会交出控制权,进入等待状态,这是协程的本质;
3)await是async wait的意思: wait的是resolve(data)的消息,并把数据data返回,比如下面代码中,当Promise对象由Pending变为Resolved的时候,变量a就等于data,然后再顺序执行下面的语句console.log(a),这真的是等待,真的是顺序执行,表现和同步代码几乎一模一样;
const a = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// async process ...
return resolve(data);
});
console.log(a);
4)await后面也可以跟同步代码: 不过系统会自动将其转化成一个Promsie对象,比如:
const a = await 'hello world'
// 相当于
const a = await Promise.resolve('hello world');
// 跟同步代码是一样的,还不如省事点,直接去掉await关键字
const a = 'hello world';
5)await对于失败消息的处理: await只关心异步过程成功的消息resolve(data),拿到相应的数据data,至于失败消息reject(error),不关心不处理;对于错误的处理有以下几种方法供选择: (1)让await后面的Promise对象自己catch; (2)也可以让外面的async函数返回的Promise对象统一catch; (3)像同步代码一样,放在一个try…catch结构中;
async componentDidMount() { // 这是React Native的回调函数,加个async关键字,没有任何影响,但是可以用await关键字
// 将异步和同步的代码放在一个try..catch中,异常都能抓到
try {
let array = null;
let data = await asyncFunction(); // 这里用await关键字,就能拿到结果值;否则,没有await的话,只能拿到Promise对象
if (array.length > 0) { // 这里会抛出异常,下面的catch也能抓到
array.push(data);
}
} catch (error) {
alert(JSON.stringify(error))
}
}
6)await对于结果的处理: await是个运算符,用于组成表达式,await表达式的运算结果取决于它等的东西,如果它等到的不是一个Promise对象,那么await表达式的运算结果就是它等到的东西;如果它等到的是一个Promise对象,await就忙起来了,它会阻塞其后面的代码,等着Promise对象resolve,然后得到resolve的值,作为await表达式的运算结果;虽然是阻塞,但async函数调用并不会造成阻塞,它内部所有的阻塞都被封装在一个Promise对象中异步执行,这也正是await必须用在async函数中的原因;
Axios
简介:ajax的升级版
Axios 是一个基于 Promise 的 HTTP 库,可以用在浏览器和 node.js 中;是请求资源的模块;通过promise对ajax的封装。 简单理解为:封装好的、基于promise的发送请求的方法,因此不用设置回调函数,直接去调用then方法。
axios是通过Promise实现对ajax技术的一种封装,就像jquery对ajax的封装一样,axios回来的数据是promise,ajax回来的数据是回调,axios比ajax更好用更安全。
简单来说就是ajax技术实现了局部数据的刷新,axios实现了对ajax的封装;axios有的ajax都有,ajax有的axios不一定有。
总结一句话就是axios是ajax,ajax不止axios。
常用方法
create创建实例 默认get
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
timeout: 1000,
headers: {'X-Custom-Header': 'foobar'}
});
instance.get('user/profile')
axios#request(config)
axios#get(url[, config])
axios#delete(url[, config])
axios#head(url[, config])
axios#options(url[, config])
axios#post(url[, data[, config]])
axios#put(url[, data[, config]])
axios#patch(url[, data[, config]])
axios#getUri([config])
Get
// 为给定 ID 的 user 创建请求
axios.get('/user?ID=12345')
//处理成功地情况 简化写法 axios.get().then(response=>{})
//response为成功返回的数据
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
//处理错误的情况
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
})
//根据参数不同,为不同处理情况
.then(function(){
});
// 可选地,上面的请求可以这样做
axios.get('/user', {
params: {
ID: 12345
}
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
export function doEdiLogin() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
axios.get("webresources/login/fileUreportList/loginEdiSystem").then(response => {
if (response.data.code === '-1') {
ElementUI.Message({
message: response.data.message,
type: 'error'
});
return reject()
} else {
return resolve()
}
}).catch((err) => {
console.log(err)
});
})
}
Post
axios.post('/user', {
firstName: 'Fred',
lastName: 'Flintstone'
})
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
});
this.$http.post('/webresources/login/activity/FileUreportResource/ureportExportUrl', {
'urlParam': urlParam,
'vuePath': vuePath
}).then(response => {
if (response.data.code === '-1') {
this.$message({
type: 'error',
message: response.data.message
})
return
}
window.open(response.data, '_target')
}).catch((err) => {
console.log(err)
})
响应结构
拦截器
在请求或响应被 then 或 catch 处理前拦截它们。
// 添加请求拦截器
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
// 在发送请求之前做些什么
return config;
}, function (error) {
// 对请求错误做些什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// 添加响应拦截器
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
// 对响应数据做点什么
return response;
}, function (error) {
// 对响应错误做点什么
return Promise.reject(error);
});
易混语法
-
axios(config)=axios.request(config) 通用/最本质的发任意类型请求的方式 默认get请求
-
axios.create(config)
- 根据指定配置创建一个新的 axios ,也就是每个axios 都有自己的配置
- 新的 axios 只是没有 取消请求 和 批量请求 的方法,其它所有语法都是一致的
- 为什么要这种语法?
- 需求,项目中有部分接口需要的配置与另一部分接口的配置不太一样
- 解决:创建2个新的 axios ,每个都有自己的配置,分别对应不同要求的接口请求中
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL:"http://localhost:3000"
})
// 使用instance发请求
instance({
url:"/posts"
})
// 或
instance.get("/posts")
实战
以vue-admin为例
-
@/utils/reuqest.js 创建一个axios实例
import axios from 'axios' import { MessageBox, Message } from 'element-ui' import store from '@/store' import { getToken } from '@/utils/auth' // create an axios instance const service = axios.create({ baseURL: process.env.VUE_APP_BASE_API, // url = base url + request url // withCredentials: true, // send cookies when cross-domain requests timeout: 5000 // request timeout }) // request interceptor service.interceptors.request.use( config => { // do something before request is sent if (store.getters.token) { // let each request carry token // ['X-Token'] is a custom headers key // please modify it according to the actual situation config.headers['X-Token'] = getToken() } return config }, error => { // do something with request error console.log(error) // for debug return Promise.reject(error) } ) // response interceptor service.interceptors.response.use( /** * If you want to get http information such as headers or status * Please return response => response */ /** * Determine the request status by custom code * Here is just an example * You can also judge the status by HTTP Status Code */ response => { const res = response.data // if the custom code is not 20000, it is judged as an error. if (res.code !== 20000) { Message({ message: res.message || 'Error', type: 'error', duration: 5 * 1000 }) // 50008: Illegal token; 50012: Other clients logged in; 50014: Token expired; if (res.code === 50008 || res.code === 50012 || res.code === 50014) { // to re-login MessageBox.confirm('You have been logged out, you can cancel to stay on this page, or log in again', 'Confirm logout', { confirmButtonText: 'Re-Login', cancelButtonText: 'Cancel', type: 'warning' }).then(() => { store.dispatch('user/resetToken').then(() => { location.reload() }) }) } return Promise.reject(new Error(res.message || 'Error')) } else { return res } }, error => { console.log('err' + error) // for debug Message({ message: error.message, type: 'error', duration: 5 * 1000 }) return Promise.reject(error) } ) export default service -
@/api/user.js (具体用户请求实例)
import request from '@/utils/request' export function login(data) { return request({ url: '/vue-element-admin/user/login', method: 'post', data }) } export function getInfo(token) { return request({ url: '/vue-element-admin/user/info', method: 'get', params: { token } }) } export function logout() { return request({ url: '/vue-element-admin/user/logout', method: 'post' }) } -
@/store/modules/user.js (管理用户的状态)
import { login, logout, getInfo } from '@/api/user'
import { getToken, setToken, removeToken } from '@/utils/auth'
import router, { resetRouter } from '@/router'
const state = {
token: getToken(),
name: '',
avatar: '',
introduction: '',
roles: []
}
//同步操作
const mutations = {
SET_TOKEN: (state, token) => {
state.token = token
},
SET_INTRODUCTION: (state, introduction) => {
state.introduction = introduction
},
SET_NAME: (state, name) => {
state.name = name
},
SET_AVATAR: (state, avatar) => {
state.avatar = avatar
},
SET_ROLES: (state, roles) => {
state.roles = roles
}
}
//异步操作
const actions = {
// user login
login({ commit }, userInfo) {
const { username, password } = userInfo
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//相当于request.get('/vue-element-admin/user/login',{username,password})
//若成功,返回的值为reponse响应值
login({ username: username.trim(), password: password }).then(response => {
//const data = reponse.data
const { data } = response
//保存状态变量
commit('SET_TOKEN', data.token)
setToken(data.token)
resolve()
}).catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
// get user info
getInfo({ commit, state }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
getInfo(state.token).then(response => {
const { data } = response
if (!data) {
reject('Verification failed, please Login again.')
}
const { roles, name, avatar, introduction } = data
// roles must be a non-empty array
if (!roles || roles.length <= 0) {
reject('getInfo: roles must be a non-null array!')
}
commit('SET_ROLES', roles)
commit('SET_NAME', name)
commit('SET_AVATAR', avatar)
commit('SET_INTRODUCTION', introduction)
resolve(data)
}).catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
// user logout
logout({ commit, state, dispatch }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
logout(state.token).then(() => {
commit('SET_TOKEN', '')
commit('SET_ROLES', [])
removeToken()
resetRouter()
// reset visited views and cached views
// to fixed https://github.com/PanJiaChen/vue-element-admin/issues/2485
dispatch('tagsView/delAllViews', null, { root: true })
resolve()
}).catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
// remove token
resetToken({ commit }) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
commit('SET_TOKEN', '')
commit('SET_ROLES', [])
removeToken()
resolve()
})
},
// dynamically modify permissions
async changeRoles({ commit, dispatch }, role) {
const token = role + '-token'
commit('SET_TOKEN', token)
setToken(token)
const { roles } = await dispatch('getInfo')
resetRouter()
// generate accessible routes map based on roles
const accessRoutes = await dispatch('permission/generateRoutes', roles, { root: true })
// dynamically add accessible routes
router.addRoutes(accessRoutes)
// reset visited views and cached views
dispatch('tagsView/delAllViews', null, { root: true })
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
-
@/views/login/index.vue
<template> <div class="login-container"> <el-form ref="loginForm" :model="loginForm" :rules="loginRules" class="login-form" autocomplete="on" label-position="left"> <div class="title-container"> <h3 class="title">Login Form</h3> </div> <el-form-item prop="username"> <span class="svg-container"> <svg-icon icon-class="user" /> </span> <el-input ref="username" v-model="loginForm.username" placeholder="Username" name="username" type="text" tabindex="1" autocomplete="on" /> </el-form-item> <el-tooltip v-model="capsTooltip" content="Caps lock is On" placement="right" manual> <el-form-item prop="password"> <span class="svg-container"> <svg-icon icon-class="password" /> </span> <el-input :key="passwordType" ref="password" v-model="loginForm.password" :type="passwordType" placeholder="Password" name="password" tabindex="2" autocomplete="on" @keyup.native="checkCapslock" @blur="capsTooltip = false" @keyup.enter.native="handleLogin" /> <span class="show-pwd" @click="showPwd"> <svg-icon :icon-class="passwordType === 'password' ? 'eye' : 'eye-open'" /> </span> </el-form-item> </el-tooltip> <el-button :loading="loading" type="primary" style="width:100%;margin-bottom:30px;" @click.native.prevent="handleLogin">Login</el-button> <div style="position:relative"> <div class="tips"> <span>Username : admin</span> <span>Password : any</span> </div> <div class="tips"> <span style="margin-right:18px;">Username : editor</span> <span>Password : any</span> </div> <el-button class="thirdparty-button" type="primary" @click="showDialog=true"> Or connect with </el-button> </div> </el-form> <el-dialog title="Or connect with" :visible.sync="showDialog"> Can not be simulated on local, so please combine you own business simulation! ! ! <br> <br> <br> <social-sign /> </el-dialog> </div> </template> <script> import { validUsername } from '@/utils/validate' import SocialSign from './components/SocialSignin' export default { name: 'Login', components: { SocialSign }, data() { const validateUsername = (rule, value, callback) => { if (!validUsername(value)) { callback(new Error('Please enter the correct user name')) } else { callback() } } const validatePassword = (rule, value, callback) => { if (value.length < 6) { callback(new Error('The password can not be less than 6 digits')) } else { callback() } } return { loginForm: { username: 'admin', password: '111111' }, loginRules: { username: [{ required: true, trigger: 'blur', validator: validateUsername }], password: [{ required: true, trigger: 'blur', validator: validatePassword }] }, passwordType: 'password', capsTooltip: false, loading: false, showDialog: false, redirect: undefined, otherQuery: {} } }, watch: { $route: { handler: function(route) { const query = route.query if (query) { this.redirect = query.redirect this.otherQuery = this.getOtherQuery(query) } }, immediate: true } }, created() { // window.addEventListener('storage', this.afterQRScan) }, mounted() { if (this.loginForm.username === '') { this.$refs.username.focus() } else if (this.loginForm.password === '') { this.$refs.password.focus() } }, destroyed() { // window.removeEventListener('storage', this.afterQRScan) }, methods: { checkCapslock(e) { const { key } = e this.capsTooltip = key && key.length === 1 && (key >= 'A' && key <= 'Z') }, showPwd() { if (this.passwordType === 'password') { this.passwordType = '' } else { this.passwordType = 'password' } this.$nextTick(() => { this.$refs.password.focus() }) }, handleLogin() { this.$refs.loginForm.validate(valid => { if (valid) { this.loading = true //调用@/store/modules/user.js里的action:login this.$store.dispatch('user/login', this.loginForm) .then(() => { //成功则跳转路由 this.$router.push({ path: this.redirect || '/', query: this.otherQuery }) this.loading = false }) //失败则状态为false .catch(() => { this.loading = false }) } else { console.log('error submit!!') return false } }) }, getOtherQuery(query) { return Object.keys(query).reduce((acc, cur) => { if (cur !== 'redirect') { acc[cur] = query[cur] } return acc }, {}) } // afterQRScan() { // if (e.key === 'x-admin-oauth-code') { // const code = getQueryObject(e.newValue) // const codeMap = { // wechat: 'code', // tencent: 'code' // } // const type = codeMap[this.auth_type] // const codeName = code[type] // if (codeName) { // this.$store.dispatch('LoginByThirdparty', codeName).then(() => { // this.$router.push({ path: this.redirect || '/' }) // }) // } else { // alert('第三方登录失败') // } // } // } } } </script> <style lang="scss"> </style> <style lang="scss" scoped> </style>
Vue router
作用:
Vue Router路由常常用于对组件进行映射与跳转。如此更方便我们实现不同页面组件的切换而实现传统网页a链接跳转的相似功能,也支持我们对子组件进行管理、放置。
- 普通路由
import Home from './components/home.vue'
const routers = [
{
path: '/home',
name: 'home',
component: Home
}, {
path: '/',
component: Home
},
]export default routers
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import routers from './routers'
import App from './App'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
routes: routers
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
render: h => h(App)
})
-
动态路由
-
嵌套路由
import Home from './components/home.vue' import First from './components/children/first.vue' import Login from './components/children/login.vue' const routers = [ { path: '/', component: Home, children: [ { path: '/', component: Login } ] }, { path: '/home', name: 'home', component: Home, children: [ { path: '/', name: 'login', component: Login }, { path: 'first', name: 'first', component: First } ] } ] export default routers -
编程式导航
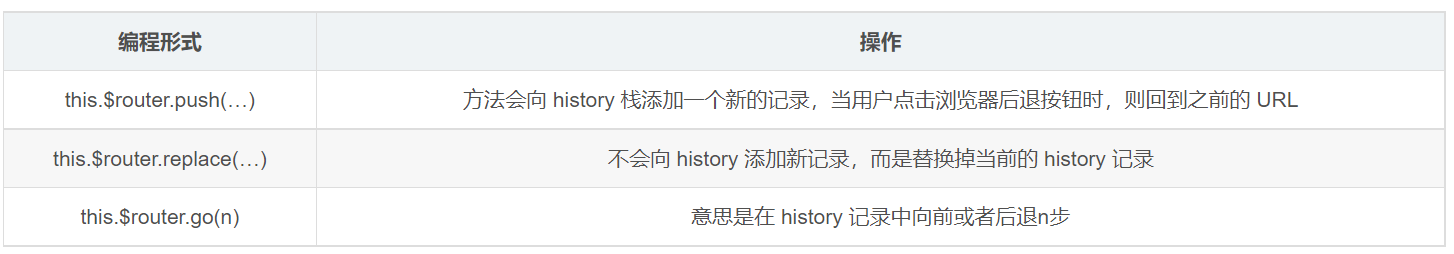
this.$router.push(…)实现路由跳转
1: 不带参数
this.$router.push('/home');
this.$router.push({name: 'home'});
this.$router.push({path: '/home'});
2: query 携带参数
this.$router.push({name: 'home', query: {id: '1'});
this.$router.push({path: 'home', query: {id: '1'});
取参数: $router.query.id
取参数: this.$router.query.id
3: 传递参数: 传参
this.$router.push({name: 'home', params: {id: '1'}});
路由配置参数: path: "/home/:id" 或者 path: "/home:id"
不配置path: 刷新页面id可能会消失。
html 取 $router.params.id
script: 脚本取参: $this.$router.params.id;
4: query 和 params 的区别:
query 类似于get, 跳转页面之后, ur了参数后边会拼接参数, 类似: id=1; 非常重要性这样可以传下去, 密码之类还是用params 刷新页面id 还是存在到但是 params 类似post 请求, 跳转页面之后, url不会拼接参数, 但是刷新页面id 会消失。
路由元信息 meta
路由定义中meta字段的作用:可以将任意信息附加到路由上,如过渡名称、谁可以访问路由(权限)等。这些事情都可以通过接收属性对象的meta属性来实现,并且它可以在路由地址和导航守卫上都被访问到。
按需加载组件
像vue这种单页面应用,如果没有应用懒加载,运用webpack打包后,一般情况下,会放在一个单独的js文件中。但是,如果很多的页面都放在同一个js文件中,必然会造成这个页面非常大,造成进入首页时,需要加载的内容过多,时间过长,会出现长时间的白屏,即使做了loading也是不利于用户体验,而运用懒加载则可以将页面进行划分,需要的时候加载页面,可以有效的分担首页所承担的加载压力,减少首页加载用时。 路由懒加载有着诸如:“只有第一次会加载页面,以后的每次页面切换,只需要进行组件替换。减少了请求体积,加快页面的响应速度,降低了对服务器的压力”等等优点。 为了解决上面的问题,我们需要对Vue实现组件懒加载(按需加载)。 前端开发使用Vue框架 路由这一块默认是这样的这样的
import HelloWord from '@/components/HelloWord'
import Login from '@/components/Login'
import Index from '@/components/Index'
这样做的结果就是webpack在npm run build的时候会打包成一个整个的js文件,如果页面一多,会导致这个文件非常大,加载缓慢,为了解决这个问题,需要将他分成多个小文件,而且还要实现异步按需加载,即用到了再加载,而不用一股脑全部加载,最常用方法:
const Login=()=>import('../component/login/login')
{
path:'/login',
name:'Login',
component:Login
}
{
path: '/guide',
component: Layout,
redirect: '/guide/index',
children: [
{
path: 'index',
component: () => import('@/views/guide/index'),
name: 'Guide',
meta: { title: 'Guide', icon: 'guide', noCache: true }
}
]
},
路由守卫
1.作用:对路由进行权限控制
2.分类:全局路由守卫,独享路由守卫,组件内路由守卫
以vue-admin-ui为例:
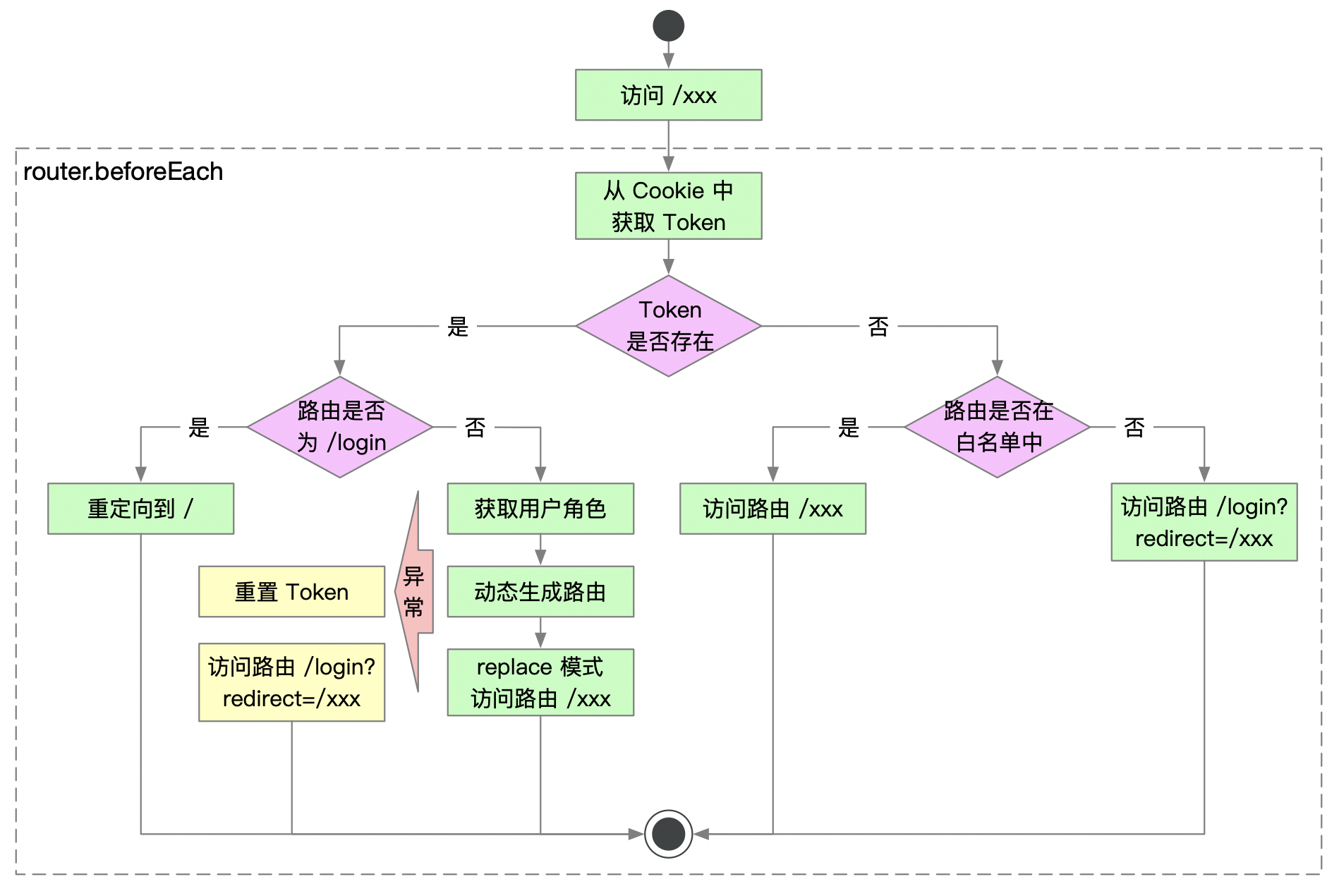
全局守卫 @/permission.js
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
import { Message } from 'element-ui'
import NProgress from 'nprogress' // progress bar
import 'nprogress/nprogress.css' // progress bar style
import { getToken } from '@/utils/auth' // get token from cookie
import getPageTitle from '@/utils/get-page-title'
NProgress.configure({ showSpinner: false }) // NProgress Configuration
const whiteList = ['/login', '/auth-redirect'] // no redirect whitelist
// 全局前置路由守卫:初始化时执行、每一次路由切换之前调用
//to和from都是路由对象
// next() //没有next所有的路由跳转都无效
router.beforeEach(async(to, from, next) => {
// start progress bar
NProgress.start()
// set page title
document.title = getPageTitle(to.meta.title)
// determine whether the user has logged in
//从cookie获取token
const hasToken = getToken()
if (hasToken) {
if (to.path === '/login') {
// if is logged in, redirect to the home page
next({ path: '/' })
NProgress.done() // hack: https://github.com/PanJiaChen/vue-element-admin/pull/2939
} else {
// determine whether the user has obtained his permission roles through getInfo
const hasRoles = store.getters.roles && store.getters.roles.length > 0
//判断用户角色是否存在
if (hasRoles) {
next()
} else {
try {
// get user info
// note: roles must be a object array! such as: ['admin'] or ,['developer','editor']
//异步获取用户角色
const { roles } = await store.dispatch('user/getInfo')
// generate accessible routes map based on roles
//根据用户角色,动态生成路由
const accessRoutes = await store.dispatch('permission/generateRoutes', roles)
// dynamically add accessible routes
//rooter.addRoutes:Dynamically add more routes to the router. The argument must be an Array using the same route config format with the routes constructor option.
router.addRoutes(accessRoutes)
// hack method to ensure that addRoutes is complete
// set the replace: true, so the navigation will not leave a history record
next({ ...to, replace: true })
} catch (error) {
// remove token and go to login page to re-login
await store.dispatch('user/resetToken')
Message.error(error || 'Has Error')
next(`/login?redirect=${to.path}`)
NProgress.done()
}
}
}
} else {
/* has no token*/
if (whiteList.indexOf(to.path) !== -1) {
// in the free login whitelist, go directly
next()
} else {
// other pages that do not have permission to access are redirected to the login page.
next(`/login?redirect=${to.path}`)
NProgress.done()
}
}
})
//全局后置路由守卫
router.afterEach(() => {
// finish progress bar
NProgress.done()
})
-
创建vue实例的时候将vue-router挂载,但这个时候vue-router挂载一些登录或者不用权限的公用的页面。
-
当用户登录后,获取用role,将role和路由表每个页面的需要的权限作比较,生成最终用户可访问的路由表。
-
调用router.addRoutes(store.getters.addRouters)添加用户可访问的路由。
-
使用vuex管理路由表,根据vuex中可访问的路由渲染侧边栏组件。
独享路由守卫
{
path: '/test',
name: 'test',
component: () => import('../views/Test.vue'),
meta:{
isAuth:true,
title:'测试'
},
//独享路由守卫(注意:没有独享后置路由守卫,他可以配合全局后置路由守卫)
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
if(to.meta.isAuth){ //判断是否需要鉴权
if(localStorage.getItem('school')==='atguigu'){ //权限控制的具体规则
next()
}else{
alert('暂无权限查看')
}
}else{
next()
}
}
},
组件内路由守卫
组件内路由守卫和全局前置后置守卫还不一样,组件内守卫包括进入组件之前调用beforeRouteEnter和离开组件时调用beforeRouteLeave,这里的离开组件时并不是全局后置路由守卫,而是指,当前组件被切换到其他组件时。
router=>index.js
{
path: '/void',
name: 'void',
component: () => import('../views/Void.vue'),
meta:{
isAuth:ture, //是否需要权限校验
title:'新闻', //用于修改网页标题
}
},
views=>Void.vue
<script>
import Category from '@/components/Category.vue'
export default {
name:'Void',
components:{ Category},
//通过路由规则,进入改组件时被调用
beforeRouteEnter(to,from,next){
console.log('beforeRouteEnter',to,from);//to一定是本组件的路由
if(to.meta.isAuth){ //判断是否需要鉴权,就不用to.path === '/home/news' || to.path === '/home/msg'
if(localStorage.getItem('school')==='atguigu'){ //权限控制的具体规则
next()
}else{
alert('暂无权限查看')
}
}else{
next()
}
},
//通过路由规则,离开该组件时被调用
beforeRouteLeave(){
console.log('beforeRouteLeave',to,from); //from一定是本组件的路由
next()
}
}
</script>
注释:什么时通过路由规则:通过切换地址栏中的路径,而不是直接挂载到APP中首次加载时。
Vuex
这里我个人建议不要为了用 vuex 而用 vuex。就拿我司的后台项目来说,它虽然比较庞大,几十个业务模块,几十种权限,但业务之间的耦合度是很低的,文章模块和评论模块几乎是俩个独立的东西,所以根本没有必要使用 vuex 来存储data,每个页面里存放自己的 data 就行。当然有些数据还是需要用 vuex 来统一管理的,如登录token,用户信息,或者是一些全局个人偏好设置等,还是用vuex管理更加的方便,具体当然还是要结合自己的业务场景的。总之还是那句话,不要为了用vuex而用vuex!
定义:vuex是一个专为vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
类似于threadlocal里的共享变量
在vue中,store用于管理状态、共享数据以及在各个组件之间管理外部状态,store是vuex应用的核心,也就是一个容器,包含着应用中大部分的状态,更改store中的状态唯一方法是提交mutation。
vuex中一共有五个状态 State Getter Mutation Action Module
State
提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据统一放到store的state进行储存,相似与data
在vuex中state中定义数据,可以在任何组件中进行调用
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import getters from './getters'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// https://webpack.js.org/guides/dependency-management/#requirecontext
const modulesFiles = require.context('./modules', true, /\.js$/)
// you do not need `import app from './modules/app'`
// it will auto require all vuex module from modules file
const modules = modulesFiles.keys().reduce((modules, modulePath) => {
// set './app.js' => 'app'
const moduleName = modulePath.replace(/^\.\/(.*)\.\w+$/, '$1')
const value = modulesFiles(modulePath)
modules[moduleName] = value.default
return modules
}, {})
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules,
getters
})
export default store
调用:
方法一:
在标签中直接使用
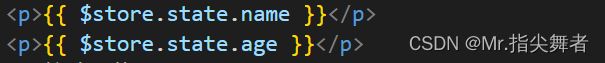
方法二:
this.$store.state.全局数据名称
方法三:
从vuex中按需导入mapstate函数
import { mapState } from "vuex";
Mutation
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type)和一个回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数:
其中参数state参数是必须的,也可以自己传递一个参数
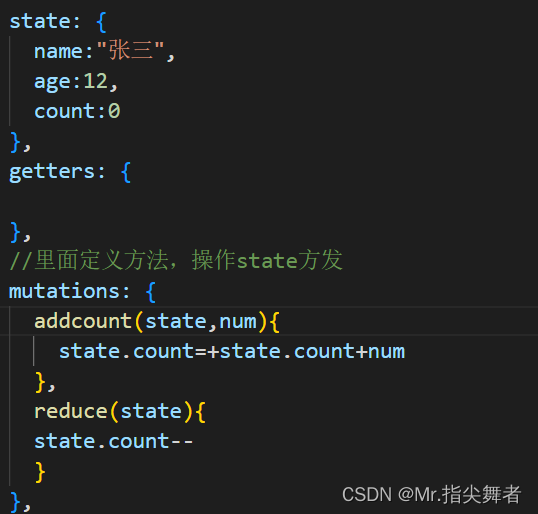
在组件中使用:
定义两个按钮进行加减操作

方法一:
注意:使用commit触发Mutation操作
methods:{
//加法
btn(){
this.$store.commit("addcount",10) //每次加十
}
//减法
btn1(){
this.$store.commit("reduce")
}
}
Action
Action和Mutation相似,Mutation 不能进行异步操作,若要进行异步操作,就得使用Action
在vuex中定义:
将上面的减法操作改为异步操作
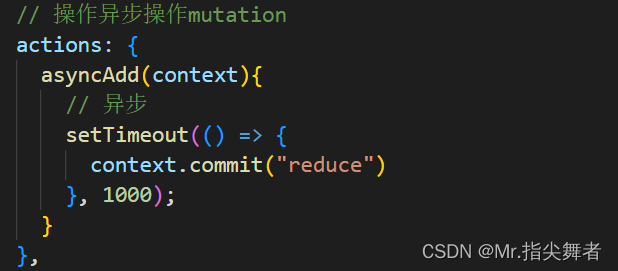
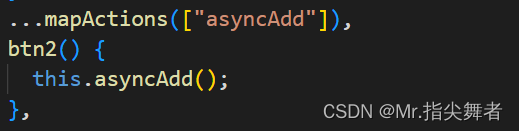
在组件中使用:
方法一:
直接使用 dispatch触发Action函数
this.$store.dispatch("reduce")
方法二:使用辅助函数
Getter
类似于vue中的computed,进行缓存,对于Store中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据
Modules
当遇见大型项目时,数据量大,store就会显得很臃肿
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割:
vue-element-admin实战分析
@/store文件夹组成:
modules文件夹(模块化开发,每个模块拥有自己的state等)、getter.js(这里是get方法,并且每次打开浏览器优先执行该方法,获取所有的状态 )、index.js
modules: app.js、errorLog.js、permission.js、setting.js、tagView.js、user.js
以user.js为例
import { login, logout, getInfo } from '@/api/user'
import { getToken, setToken, removeToken } from '@/utils/auth'
import router, { resetRouter } from '@/router'
//管理用户的各个状态信息,如token、name、avatar等
const state = {
token: getToken(),
name: '',
avatar: '',
introduction: '',
roles: []
}
//更改用户的状态信息,同步方法,通过this.$store.commit("SET_TOKEN",token)调用
const mutations = {
//state:必须的第一个参数,token根据用户传入
SET_TOKEN: (state, token) => {
state.token = token
},
SET_INTRODUCTION: (state, introduction) => {
state.introduction = introduction
},
SET_NAME: (state, name) => {
state.name = name
},
SET_AVATAR: (state, avatar) => {
state.avatar = avatar
},
SET_ROLES: (state, roles) => {
state.roles = roles
}
}
//异步方法,通过this.$store.dispatch("login")调用
const actions = {
// user login
login({ commit }, userInfo) {
const { username, password } = userInfo
//异步返回对象Promise
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//调用api.user中的login方法,axios请求地址,返回response对象
login({ username: username.trim(), password: password }).then(response => {
//es6简化写法,原为 const data = response.data
const { data } = response
//调用mutation里的set_token方法,赋予token
commit('SET_TOKEN', data.token)
//调用认证模块里的setToken方法
setToken(data.token)
resolve()
}).catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
// get user info
getInfo({ commit, state }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
getInfo(state.token).then(response => {
const { data } = response
if (!data) {
reject('Verification failed, please Login again.')
}
const { roles, name, avatar, introduction } = data
// roles must be a non-empty array
if (!roles || roles.length <= 0) {
reject('getInfo: roles must be a non-null array!')
}
commit('SET_ROLES', roles)
commit('SET_NAME', name)
commit('SET_AVATAR', avatar)
commit('SET_INTRODUCTION', introduction)
resolve(data)
}).catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
// user logout
logout({ commit, state, dispatch }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
logout(state.token).then(() => {
commit('SET_TOKEN', '')
commit('SET_ROLES', [])
removeToken()
resetRouter()
// reset visited views and cached views
// to fixed https://github.com/PanJiaChen/vue-element-admin/issues/2485
dispatch('tagsView/delAllViews', null, { root: true })
resolve()
}).catch(error => {
reject(error)
})
})
},
// remove token
resetToken({ commit }) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
commit('SET_TOKEN', '')
commit('SET_ROLES', [])
removeToken()
resolve()
})
},
// dynamically modify permissions
async changeRoles({ commit, dispatch }, role) {
const token = role + '-token'
commit('SET_TOKEN', token)
setToken(token)
const { roles } = await dispatch('getInfo')
resetRouter()
// generate accessible routes map based on roles
const accessRoutes = await dispatch('permission/generateRoutes', roles, { root: true })
// dynamically add accessible routes
router.addRoutes(accessRoutes)
// reset visited views and cached views
dispatch('tagsView/delAllViews', null, { root: true })
}
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
getter.js(存放操作变量的键值对)
const getters = {//getters的作用只是简化写法,不要用了,直接 state.user.orgnId就行,wxl
sidebar: state => state.app.sidebar,
language: state => state.app.language,
visitedViews: state => state.app.visitedViews,
cachedViews: state => state.app.cachedViews,
selectedView: state => state.app.selectedView,
token: state => state.user.token,
avatar: state => state.user.avatar,
name: state => state.user.name,
skin: state => state.user.skin,
introduction: state => state.user.introduction,
status: state => state.user.status,
roles: state => state.user.roles,
setting: state => state.user.setting,
permission_routers: state => state.permission.routers,
hdMenu: state => state.permission.hdMenu,
addRouters: state => state.permission.addRouters,
companyId: state => state.user.companyId
}
export default getters
index.js(配置并创建vuex.store)
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import getters from './getters'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// https://webpack.js.org/guides/dependency-management/#requirecontext
const modulesFiles = require.context('./modules', true, /\.js$/)
// you do not need `import app from './modules/app'`
// it will auto require all vuex module from modules file
const modules = modulesFiles.keys().reduce((modules, modulePath) => {
// set './app.js' => 'app'
const moduleName = modulePath.replace(/^\.\/(.*)\.\w+$/, '$1')
const value = modulesFiles(modulePath)
modules[moduleName] = value.default
return modules
}, {})
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules,
getters
})
export default store
/views/login/index.vue
<template>
<div class="login-container">
<el-form ref="loginForm" :model="loginForm" :rules="loginRules" class="login-form" autocomplete="on" label-position="left">
<div class="title-container">
<h3 class="title">Login Form</h3>
</div>
<el-form-item prop="username">
<span class="svg-container">
<svg-icon icon-class="user" />
</span>
<el-input
ref="username"
v-model="loginForm.username"
placeholder="Username"
name="username"
type="text"
tabindex="1"
autocomplete="on"
/>
</el-form-item>
<el-tooltip v-model="capsTooltip" content="Caps lock is On" placement="right" manual>
<el-form-item prop="password">
<span class="svg-container">
<svg-icon icon-class="password" />
</span>
<el-input
:key="passwordType"
ref="password"
v-model="loginForm.password"
:type="passwordType"
placeholder="Password"
name="password"
tabindex="2"
autocomplete="on"
@keyup.native="checkCapslock"
@blur="capsTooltip = false"
@keyup.enter.native="handleLogin"
/>
<span class="show-pwd" @click="showPwd">
<svg-icon :icon-class="passwordType === 'password' ? 'eye' : 'eye-open'" />
</span>
</el-form-item>
</el-tooltip>
// 点击按钮,触发handleLogin方法
<el-button :loading="loading" type="primary" style="width:100%;margin-bottom:30px;" @click.native.prevent="handleLogin">Login</el-button>
<div style="position:relative">
<div class="tips">
<span>Username : admin</span>
<span>Password : any</span>
</div>
<div class="tips">
<span style="margin-right:18px;">Username : editor</span>
<span>Password : any</span>
</div>
<el-button class="thirdparty-button" type="primary" @click="showDialog=true">
Or connect with
</el-button>
</div>
</el-form>
<el-dialog title="Or connect with" :visible.sync="showDialog">
Can not be simulated on local, so please combine you own business simulation! ! !
<br>
<br>
<br>
<social-sign />
</el-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { validUsername } from '@/utils/validate'
import SocialSign from './components/SocialSignin'
export default {
name: 'Login',
components: { SocialSign },
data() {
const validateUsername = (rule, value, callback) => {
if (!validUsername(value)) {
callback(new Error('Please enter the correct user name'))
} else {
callback()
}
}
const validatePassword = (rule, value, callback) => {
if (value.length < 6) {
callback(new Error('The password can not be less than 6 digits'))
} else {
callback()
}
}
return {
loginForm: {
username: 'admin',
password: '111111'
},
loginRules: {
username: [{ required: true, trigger: 'blur', validator: validateUsername }],
password: [{ required: true, trigger: 'blur', validator: validatePassword }]
},
passwordType: 'password',
capsTooltip: false,
loading: false,
showDialog: false,
redirect: undefined,
otherQuery: {}
}
},
watch: {
$route: {
handler: function(route) {
const query = route.query
if (query) {
this.redirect = query.redirect
this.otherQuery = this.getOtherQuery(query)
}
},
immediate: true
}
},
created() {
// window.addEventListener('storage', this.afterQRScan)
},
mounted() {
if (this.loginForm.username === '') {
this.$refs.username.focus()
} else if (this.loginForm.password === '') {
this.$refs.password.focus()
}
},
destroyed() {
// window.removeEventListener('storage', this.afterQRScan)
},
methods: {
checkCapslock(e) {
const { key } = e
this.capsTooltip = key && key.length === 1 && (key >= 'A' && key <= 'Z')
},
showPwd() {
if (this.passwordType === 'password') {
this.passwordType = ''
} else {
this.passwordType = 'password'
}
this.$nextTick(() => {
this.$refs.password.focus()
})
},
handleLogin() {
this.$refs.loginForm.validate(valid => {
if (valid) {
this.loading = true
//如果验证成功,调用user.js里的actions中的login方法,并传入用户登录信息
this.$store.dispatch('user/login', this.loginForm)
.then(() => {
this.$router.push({ path: this.redirect || '/', query: this.otherQuery })
this.loading = false
})
.catch(() => {
this.loading = false
})
} else {
console.log('error submit!!')
return false
}
})
},
getOtherQuery(query) {
return Object.keys(query).reduce((acc, cur) => {
if (cur !== 'redirect') {
acc[cur] = query[cur]
}
return acc
}, {})
}
// afterQRScan() {
// if (e.key === 'x-admin-oauth-code') {
// const code = getQueryObject(e.newValue)
// const codeMap = {
// wechat: 'code',
// tencent: 'code'
// }
// const type = codeMap[this.auth_type]
// const codeName = code[type]
// if (codeName) {
// this.$store.dispatch('LoginByThirdparty', codeName).then(() => {
// this.$router.push({ path: this.redirect || '/' })
// })
// } else {
// alert('第三方登录失败')
// }
// }
// }
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss">
</style>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
</style>
store的执行顺序: 打开浏览器 → getters → 组件调用actions中的方法 → mutations(设置state的值) → getters(更新数据)
$refs
- ref 加在普通的元素上,用this.$refs.(ref值) 获取到的是dom元素
- ref加在子组件上,用this.$refs(ref值 ) 获 取 到 的 是 组 件 实 例 , 可 以 使 用 组 件 的 所 有 方 法 。 在 使 用 方 法 的 时 候 直 接this.$refs.(ref值)获取到的是组件实例,可以使用组件的所有方法。在使用方法的时候直接this.refs.(ref值)获取到的是组件实例,可以使用组件的所有方法。在使用方法的时候直接this.refs.(ref值).方法() 就可以使用了
- 如何利用v-for 和 ref 获取一组数组或者dom 节点
ref 需要在dom渲染完成后才会有,在使用的时候确保dom已经渲染完成。比如在生命周期 mounted(){} 钩子中调用,或者在 this.$nextTick(()=>{}) 中调用。
install
通常用于自定义插件和注册全局注册组件
自定义组件使用
全局注册
import ... from ...
export default {
install(Vue) {
Vue.component('PageTools', PageTools)
Vue.component('update', update)
Vue.component('ImageUpload', ImageUpload)
Vue.component('ScreenFull', ScreenFull)
Vue.component('ThemePicker', ThemePicker)
Vue.component('TagsView', TagsView)
}
}
外部组件使用
src/main.js
import vueEsign from 'vue-esign'
Vue.component('vueEsign', vueEsign)
data和props的区别
data
当前组件对象操作的数据,是每个组件的私有内存,是存储数据和希望跟踪的任何其他变量的地方。
如果我们正在构建一个计数器应用程序,我们将需要跟踪计数,因此我们将向我们的data添加一个count:
<template>
<div>
{{ count }}
<button @click="increment">+</button>
<button @click="decrement">-</button>
</div>
</template>
export default {
name: 'Counter',
data() {
return {
// Initialized to zero to begin
count: 0,
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.count += 1;
},
decrement() {
this.count -= 1;
}
}
}
此处的data是私有的,仅供组件本身使用,其他组件不能访问它。
如果需要向组件传递数据,可以使用props向下传递数据(传递给子组件),或者使用事件向上传递数据(传递给父组件)。
props
可供父组件操作的属性。props 可以是数组或对象,用于接收来自父组件的数据。props 可以是简单的数组,或者使用对象作为替代,对象允许配置高级选项,如类型检测、自定义验证和设置默认值。
<template>
<my-component color-prop="hello world"></my-component>
</template>
然而,当我们从组件内部访问props时,我们并不拥有它们,所以我们不能更改它们
区别
1、data不需要用户(开发者)传值,自身维护;而props需要用户(开发者)传值。
2、data上的数据都是可读可写的;而props上的数据只可以读的,无法重新赋值。
Watch&Computed
- watch中监听props中的数据或data中的数据
- computed中计算props或者data中的数据
- data中使用props中的数据进行拷贝,如需响应数据变化则在watch中监听props的变化,在赋值给data
- 不要直接赋值给computed的属性,如果需要赋值,computed需要定义get与set函数
computed
computed的使用场景:适用于一些重复使用数据或复杂及费时的运算。我们可以把它放入computed中进行计算, 然后会在computed中缓存起来,下次就可以直接获取了。
<template>
<div>
<div>
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName" />
</div>
<div>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName" />
</div>
<!-- 调用两次fullName -->
<div>姓名:{{ fullName }}</div>
<div>姓名:{{ fullName }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
firstName: "张",
lastName: "三",
};
},
computed: {
fullName() {
console.log("这是fullName");
return this.firstName + this.lastName;
}
}
};
</script>
watch
watch用来监听数据。它会对data的数据监听回调,当依赖的data的数据变化时,会执行回调。在回调中会传入newVal和oldVal两个参数。
watch的使用场景是:当在data中的某个数据发生变化时,我们需要做一些操作, 或者当需要在数据变化时执行异步或开销较大的操作时,我们就可以使用watch来进行监听。
require 和 import
require: CommonJS语法。用于导入模块
const Clipboard = require('clipboard')
if (!Clipboard) {
throw new Error('you shold npm install `clipboard` --save at first ')
}
Filters
用于一些常见的文本格式化。也许后端返回的数据格式并不是最终想要展示出来的,通过过滤器可以进行处理成自己想要展示出来的格式。由“管道”符号指示。
在调取接口的返回数据的时候,我们经常能够得到各种Number类型的数据。
这种格式的数据,很多时候都是表明对应的类型。
如果直接返回到页面上展示,对于操作人员来讲,没有任何意义。
所以,一般的情况下,我们需要把格式对应类型的中文名称显示出来。
Directive
vue.directive的作用
vue.directive是我们除了内置的指令(如v-model和v-show)之外的自定义指令(v-自定义)。自定义指令是对普通DOM元素进行的底层操作,它是一种有效的的补充和扩展,不仅可以用于定义任何的dom操作,并且是可以复用的,
<template>
<div>
<div id="app"><input v-focus /></div>
<hr>
<p style="width:200px;height:200px" v-pin='colors'>trying</p>
<hr>
<div id="app" v-demo:foo.a.b="message"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Vue from "vue";
// 1、输入框聚焦
Vue.directive("focus", {
// 当被绑定的元素插入到 DOM 中时……
inserted: function (el) {
// 聚焦元素
el.focus();
},
});
// 2、绑定背景颜色
Vue.directive('pin', function(el, binding) { //背景颜色
el.style.background = binding.value
})
// 3、文字显示
Vue.directive('demo', {
bind: function (el, binding, vnode) {
var s = JSON.stringify
el.innerHTML =
'name: ' + s(binding.name) + '<br>' +
'value: ' + s(binding.value) + '<br>' +
'expression: ' + s(binding.expression) + '<br>' +
'argument: ' + s(binding.arg) + '<br>' +
'modifiers: ' + s(binding.modifiers) + '<br>' +
'vnode keys: ' + Object.keys(vnode).join(', ')
}
})
export default {
name: "directive",
data() {
return {
colors:"",//定义变量接收
message:'left',
}
},
created(){
this.colors="pink"
}
}
</script>
钩子函数
vue.directive有5种钩子函数,分别是:bind, inserted ,update, componentUpdated, unbind
- bind:只调用一次,指令第一次绑定到元素时调用,在这里可以进行一次性的初始化设置
- inserted:被绑定元素插入父节点时调用(仅保证父节点存在,但不一定被插入文档中)
- update:所在组件的vnode更新时调用,但是可能发生在其子vnode更新之前,指令的值可能发生了变化,也可能没有
- componentUpdate:指令所在组件的vnode及其子vnode全部更新后调用
- unbind:只调用一次,指令与元素解绑时调用
参数
el,binding(name,value,oldValue,expression,arg,modifiers), vnode,oldvnode
Mock
-
模拟请求
export default { ts: { "total": 999, "rows": [{ "recNam": "LiQiang", "recTim": "2018-07-10 22:12", "updNam": "LiQiang", "updTim": "2018-07-10 22:12", "idevVersionUse": 1531231938000, "_obj": null, "_map": {}, "fieldId": "87e8dcf411da4f409d19bf138f28fca4", "fieldName": "单证记账类型", "fieldCod": "LEDGER_CODE", "sorter": "102", "teamOrgnId": "9eb40a53de0e44429c15687bfada4a04", "teamOrgnIdStr": "二公司", "orgnId": "5f2f498bd5924734b9432ba71e35b8c7", "description": null }, { "recNam": "shisg", "recTim": "2018-04-23 13:04", "updNam": "admin", "updTim": "2018-06-22 10:52", "idevVersionUse": 1529635967125, "_obj": null, "_map": {}, "fieldId": "6A7BB06E97391CEBE0530101007F3CE8", "fieldName": "货物记账项", "fieldCod": "CARGO_ITEM", "sorter": "9", "teamOrgnId": "0", "teamOrgnIdStr": "招商局集团", "orgnId": "0", "description": null }], "footer": null } }-
mock
import Mock from 'mockjs' import loginAPI from './login' // Mock.setup({ // timeout: '350-600' // }) // 登录相关 Mock.mock('/webresources/login/privilege/SysField/find', 'post', loginAPI.ts) export default Mock
-
中期
按钮权限
自定义指令 实现动态全局按钮权限控制
-
自定义指令
//directive/permission/permission.js import store from '@/store' export default { inserted(el, binding, vnode) { const { value } = binding const permissionList = store.getters && store.getters.permissionList if (!value) return el.parentNode && el.parentNode.removeChild(el) const modelId = vnode.context._routerRoot._route.meta.modelId || '' if (!modelId) return el.parentNode && el.parentNode.removeChild(el) const list = permissionList.filter(o => o.modelId === modelId) if (!list.length) return el.parentNode && el.parentNode.removeChild(el) const btnList = list[0] && list[0].button ? list[0].button : [] if (!btnList.length) { el.parentNode && el.parentNode.removeChild(el) } else { const hasPermission = btnList.some(btn => btn.enCode === value) if (!hasPermission) { el.parentNode && el.parentNode.removeChild(el) } } } } //directive/permission/index.js import permission from './permission' const install = function(Vue) { Vue.directive('has', permission) } if (window.Vue) { window['has'] = permission Vue.use(install); // eslint-disable-line } permission.install = install export default permission //main.js import permission from "@/directive/permission"; Vue.use(permission) -
前端
<el-button v-has="btn_process" type="text" :style='{"width":"40%"}' @click="isprocess(scope.row.ship_id)" :disabled="(scope.row.isProcess)==1?true:false">审核
常见开发问题:
-
vue中不能在标签中使用插值表达式了
Interpolation inside attributes has been removed. Use v-bind or the colon shorthand instead.
解决:改用前面加上冒号
<el-tag :type="scope.row.isProcess | dynamicText(processOptions) == '已审核' ? 'success' : 'danger'" disable-transitions> {{ scope.row.isProcess | dynamicText(processOptions) }} </el-tag> -
管道
{{}}为取值符号, | 为过滤器Vue.js 允许你自定义过滤器,可被用于一些常见的文本格式化。过滤器可以用在两个地方:双花括号插值和
v-bind表达式 (后者从 2.1.0+ 开始支持)。过滤器应该被添加在 JavaScript 表达式的尾部,由“管道”符号指示:
<!-- 在双花括号中 -->
{{ message | capitalize }}
<!-- 在 `v-bind` 中 -->
<div v-bind:id="rawId | formatId"></div>